What PoC Means and Its Applications Best in Business, Technology, and Beyond 2024
In the fast-evolving landscape of technology and business, the term “PoC” frequently appears. But what does PoC mean? For anyone exploring innovative solutions, it’s essential to understand the significance of this term, especially since it drives the initial steps of projects and helps validate new concepts. In this article, we’ll break down what “PoC means,” its different applications, and why it’s crucial across industries.
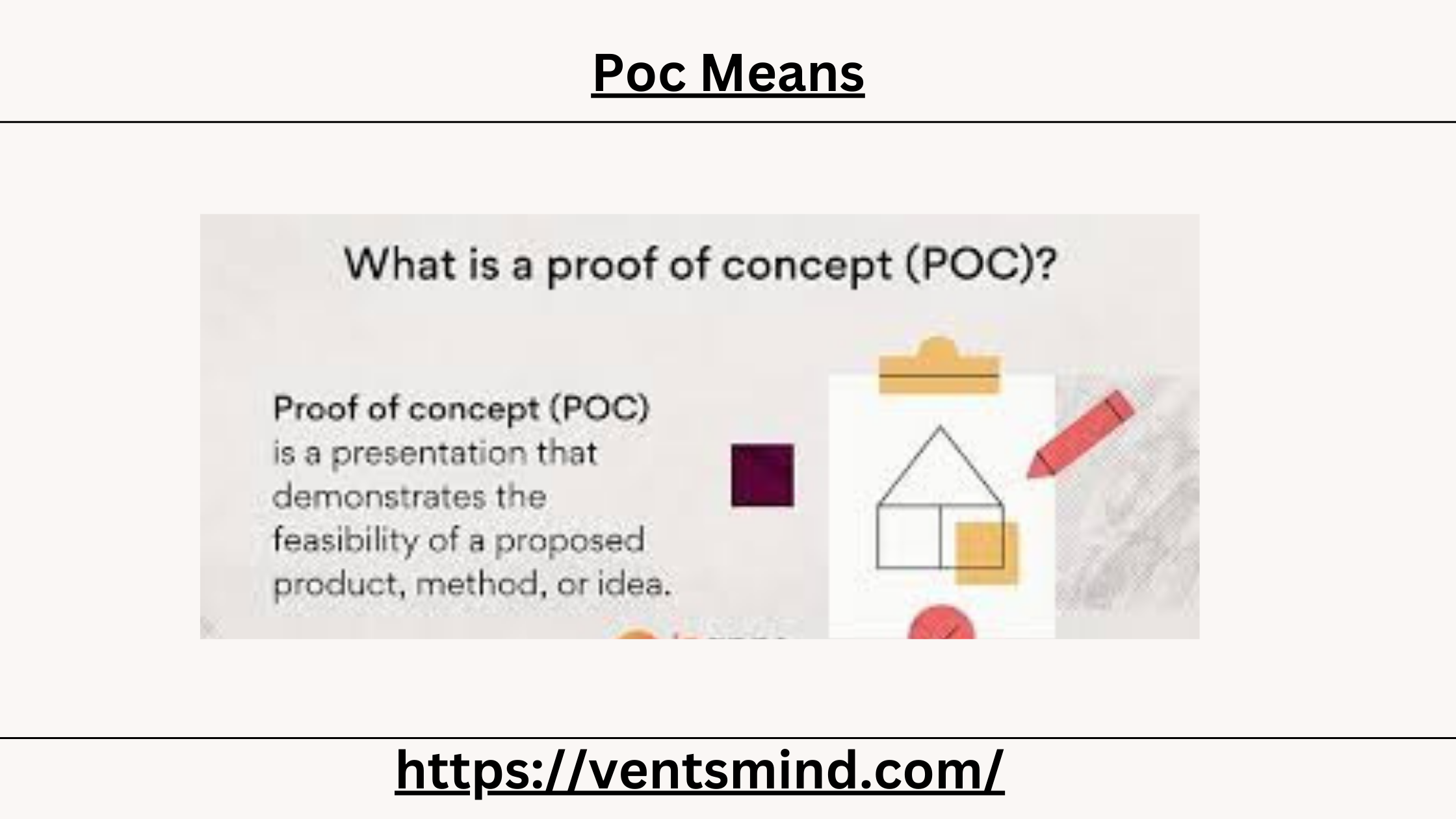
What PoC Means
To start, let’s define what PoC means. “PoC” stands for “Proof of Concept.” In simple terms, a PoC is a preliminary demonstration that validates an idea, technology, or solution’s feasibility. When we ask, “What does PoC mean?” we’re essentially asking whether a proposed solution can work in a real-world environment. A PoC allows teams to test a concept on a small scale before committing to full-scale development, saving both time and resources if the idea proves to be unfeasible.
In various fields, “PoC means” can slightly vary, but the core principle remains the same: testing an idea’s practicality. Below, we’ll explore how “PoC means” applies to different domains and why it’s an essential step in product development and innovation.
Why PoC Matters in Technology
One of the most common places where “PoC means” is widely used is in technology, especially within software development. In this context, PoC helps confirm whether a particular technology or solution can meet the technical requirements of a project. It answers critical questions like: Will this solution work in our system? Is the technology compatible with our existing tools?
In software, a PoC may involve creating a simplified version of the product that tests specific functionalities or integration capabilities. Here, “PoC means” the ability to try out ideas without investing too many resources in full development. For instance, if a company wants to incorporate artificial intelligence into its application, it could create a PoC for the AI component to determine whether it can provide the expected results.
How PoC Applies in Business Contexts
In business, the term “PoC means” often applies to evaluating new ideas, products, or services. A PoC in business helps assess market demand, feasibility, and the overall potential of a proposed solution. Companies might run a PoC to determine if customers would be interested in a new product feature or to see if a new process could reduce operational costs.
For example, a startup might create a PoC to validate its business model by launching a minimum viable product (MVP) to gauge customer interest. Here, “PoC means” the initial testing phase to confirm whether the concept has the potential for growth and scalability.
Types of PoC and What They Mean
Understanding “PoC means” requires us to look at the various types of PoC used across industries:
- Technical PoC: Often used in software development, this PoC tests whether a technical concept can be achieved within existing limitations.
- Business PoC: In business, PoC means testing an idea’s viability from a market or operational perspective, confirming demand and potential profitability.
- Pilot PoC: A small-scale trial run to test how a solution performs in a real-world setting, often used before full-scale deployment.
Each type of PoC focuses on validating a different aspect of a concept, but they all serve the purpose of reducing risk and uncertainty.
Steps to Developing a PoC
Creating a PoC involves a structured approach. When understanding “PoC means,” it’s helpful to look at how companies typically go about this process.
- Identify Objectives: Clearly define what you hope to achieve. Understanding “PoC means” also involves knowing what success looks like for your project.
- Design the Scope: Determine the PoC’s scope to avoid excessive time and resource investment. Since “PoC means” testing on a small scale, avoid overcomplicating it.
- Set Metrics for Success: Define measurable criteria to evaluate whether the PoC achieves its intended purpose.
- Develop the PoC: Build the minimal viable version of the concept.
- Test and Gather Feedback: Run the PoC and gather data to assess if the concept meets the predefined metrics.
- Make a Decision: Based on the results, decide if the concept is worth scaling up.
PoC Means for Entrepreneurs and Startups
For entrepreneurs and startups, understanding “PoC means” can significantly impact their chances of success. Developing a PoC allows startups to test their ideas with minimal financial risk. By launching a PoC, entrepreneurs can validate their product, gather user feedback, and adjust before fully committing resources.
Startups can use a PoC to attract investors by demonstrating that their idea has potential. In this context, “PoC means” a necessary first step toward proving to investors that their idea is viable.
PoC Means in Cybersecurity
In cybersecurity, “PoC means” something slightly different but equally crucial. Here, a PoC often refers to testing the effectiveness of a security measure or the impact of a vulnerability. For instance, when researchers discover a new security flaw, they might create a PoC to show how it could be exploited. This PoC can help cybersecurity teams understand the vulnerability’s scope and urgency.
For security teams, understanding “PoC means” is essential to implementing proactive measures. By running a PoC for a security solution, companies can evaluate whether it can effectively protect their systems.
The Benefits of PoC in Product Development
In product development, understanding “PoC means” is crucial as it allows teams to verify ideas without diving into full-scale production. This approach has several benefits:
- Risk Reduction: Testing a concept early reduces the risk of investing in ideas that may fail.
- Cost Efficiency: PoC requires minimal resources compared to full-scale development, making it a cost-effective way to validate ideas.
- Faster Time-to-Market: PoCs can help teams quickly determine the best way to move forward, expediting product development.
- Enhanced Collaboration: When stakeholders understand what “PoC means,” it fosters collaboration and better alignment of expectations.
Limitations of PoC
While PoCs are valuable, it’s important to recognize their limitations. PoCs are typically limited in scope, meaning they may not fully capture the complexities of a large-scale deployment. Additionally, the results of a PoC might not always be conclusive; some ideas may work in controlled environments but face challenges when scaled.
Understanding “PoC means” recognizing these limitations and using PoC results as a guide rather than an absolute predictor of success.
Examples of PoC in Real-World Applications
To further clarify what PoC means, let’s look at some examples from different industries:
- Healthcare: A company may develop a PoC for a new medical device to test its effectiveness in a clinical setting before moving to full production.
- Retail: Retailers might launch a PoC for an augmented reality app that lets customers visualize products in their homes.
- Finance: Banks use PoCs to test blockchain solutions for secure transactions before fully implementing them.
- Manufacturing: A manufacturer could run a PoC to test robotic automation, measuring efficiency and quality improvements in a controlled setting.
PoC Means and Innovation: Embracing Change
One reason why “PoC means” has become so prevalent is its role in fostering innovation. By providing a low-risk platform for experimentation, PoCs encourage teams to think outside the box and explore new ideas. For organizations committed to growth, understanding what “PoC means” can be the difference between leading the market and being left behind.
PoCs make it easier for teams to pivot based on data, allowing them to abandon unpromising ideas or refine them into something viable. In this sense, PoC means embracing an experimental mindset that values feedback and agility.
Conclusion: PoC Means a Path to Feasibility and Innovation
In summary, “PoC means” testing, validating, and, if necessary, refining ideas in a manageable, cost-effective way. Whether in technology, business, cybersecurity, or healthcare, PoCs allow teams to reduce risks, explore potential, and make informed decisions about moving forward. For startups and established businesses alike, understanding what PoC means is a key part of staying competitive and innovating effectively.
From technical validation to business feasibility, PoC means the gateway to smarter, more strategic innovation across all sectors. By understanding and applying the concept of PoC, organizations can navigate the complexities of the modern world with confidence and clarity.


