Website Portal: Best Guide to Benefits, Features, and Uses In 2024
In today’s digital age, the need for streamlined communication, data accessibility, and efficient management of information has given rise to the concept of a website portal. Whether it’s a business trying to manage its clients, an educational institution handling student data, or a government organization ensuring seamless public services, the website portal plays a vital role in managing and disseminating information effectively.
This article delves into the core concepts, benefits, types, and key features of a website portal while highlighting how it has become an essential tool for organizations and individuals alike.
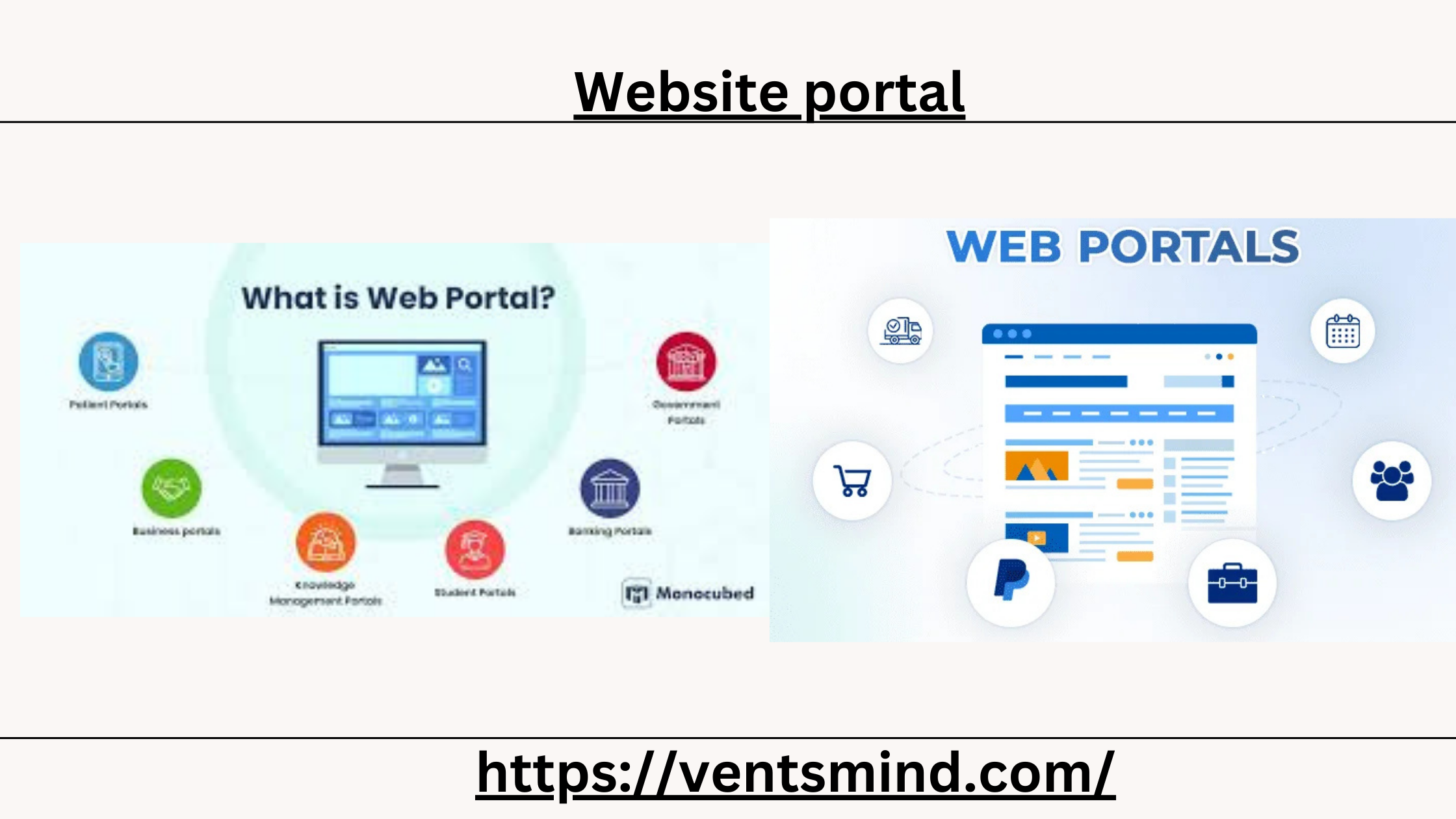
What is a Website Portal?
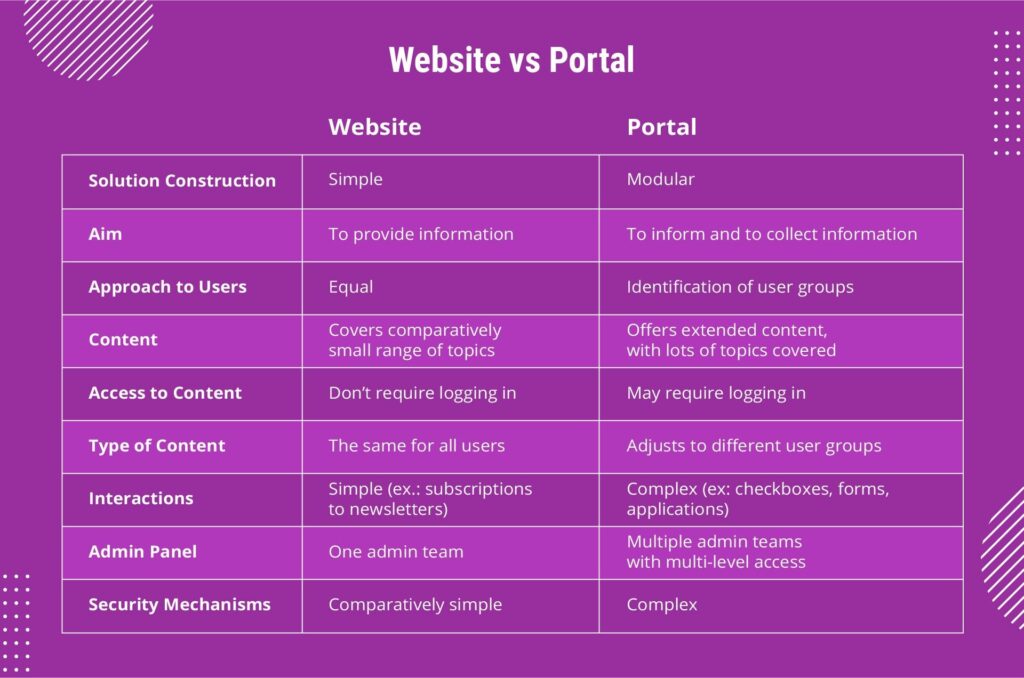
A website portal is essentially a centralized online platform that offers a variety of services, tools, and resources to specific users. Typically, a website portal functions as a gateway to a range of information or services, which are customized based on the user’s profile or role within an organization.
In contrast to a standard website, which provides generic information to all visitors, a website portal delivers personalized content based on user credentials, preferences, or needs. For example, a company’s intranet portal might provide employees access to internal documents, project management tools, and communication platforms, whereas a customer-facing portal might allow clients to track orders, check service status, or interact with customer support.
Key Features of a Website Portal
A well-designed portal offers several distinct features that set it apart from a basic website:
- User Authentication and Access Control: Users need to log in with unique credentials. This ensures security and allows the portal to display tailored information based on user roles.
- Personalized Content: Once logged in, users can access personalized content and resources specific to their profile. This could be anything from a dashboard of financial data to a student’s academic records.
- Collaboration Tools: Most website portals offer communication and collaboration tools like messaging systems, discussion boards, or team workspaces that help users interact and share information seamlessly.
- Document Management: A robust document management system is often embedded within a portal. This allows users to upload, download, and manage files in an organized and secure manner.
- Self-Service Functions: Whether it’s employees submitting leave applications or customers tracking orders, portals enable users to perform tasks independently, reducing the need for human intervention.
- Scalability: A website portal can grow with the organization. Its features can be expanded as the user base grows or as additional functionality is needed.
- Integration with Other Systems: Often, website portals are integrated with other software systems such as CRMs (Customer Relationship Management) and ERPs (Enterprise Resource Planning), providing a seamless user experience.
Types of Website Portals
There are several types of website portals, each catering to different needs and audiences. The most common ones include:
- Employee Intranet Portals: These portals are designed for internal use within organizations. They serve as a hub where employees can access internal communications, HR information, project updates, and more. An employee intranet portal fosters collaboration, improves productivity, and ensures everyone in the organization is on the same page.
- Customer Portals: A customer portal is a type of portal that provides clients or customers with access to personalized information and services. Customers can log in to check order statuses, view invoices, raise support tickets, and much more. This not only enhances customer satisfaction but also reduces the need for customer support personnel.
- Supplier or Vendor Portals: These portals are built for suppliers and vendors to streamline procurement and supply chain management. Vendors can view purchase orders, track payments, and update their details, while businesses can track inventory, manage contracts, and evaluate supplier performance.
- Educational Portals: A website portal for educational institutions allows students, faculty, and administrative staff to access important resources. Students can register for classes, check grades, and communicate with instructors, while faculty can manage class rosters and upload course materials.
- Government Portals: These portals are designed to deliver public services online, providing citizens access to important government resources. For example, citizens can apply for permits, renew licenses, and pay taxes through a website portal that centralizes various services.
- Community Portals: Often designed for a specific group or community, these portals allow members to collaborate, share ideas, or even access unique content. A community website portal can range from fan communities to professional networks.
Advantages of Using a Website Portal
The adoption of a website portal comes with numerous benefits, which enhance user experience and organizational efficiency.
1. Centralized Information Management
A website portal centralizes information, making it easier for users to find what they need. This means employees can access company policies, clients can view past orders, and students can check their grades—all from one location. This centralization reduces the need for repetitive communication and minimizes errors.
2. Enhanced User Experience
Users enjoy the convenience of accessing everything they need from a single website portal. This streamlined approach to data and services ensures a better user experience, which leads to higher satisfaction and engagement rates.
3. Cost-Effectiveness
By allowing users to self-service for tasks such as managing their profiles, submitting forms, or checking statuses, website portals reduce the need for manual processes and administrative support. Over time, this leads to significant cost savings for organizations.
4. Improved Communication and Collaboration
A website portal is a central place where communication can happen. It can feature chat options, discussion boards, and messaging systems, enabling teams to collaborate effectively. This feature is particularly beneficial in remote work environments, where teams rely on digital communication tools to stay connected.
5. Better Security
Since users log in to a website portal with unique credentials, it ensures that sensitive information is accessible only to authorized individuals. Additionally, most portals include encryption and other security measures to protect data.
6. Scalability and Flexibility
As your organization grows, a website portal can be easily scaled to accommodate more users and offer additional functionality. Whether it’s adding new services for customers or integrating with more tools, a portal evolves with your needs.
7. Increased Productivity
With the right tools and resources available in one place, employees can complete tasks more efficiently, clients can resolve issues faster, and students can find relevant course materials with ease. This leads to improved productivity across the board.
How to Build an Effective Website Portal
Building a website portal that effectively serves its users requires careful planning and the right technology stack. Below are some key steps to follow:
1. Identify Your Users and Their Needs
Understanding your users is crucial. Whether you are building a customer portal, employee intranet, or educational platform, your website portal should meet the specific needs of its target audience. Conduct surveys or focus groups to identify the tools and resources users need the most.
2. Choose the Right Platform
There are several platforms available for building a website portal, from open-source solutions like WordPress with portal plugins to enterprise-grade platforms like Microsoft SharePoint. The platform you choose will depend on your budget, scalability requirements, and specific features needed.
3. Integrate with Other Systems
To provide a seamless experience, ensure your website portal integrates with other systems you use, such as CRM, ERP, or HR software. This allows for real-time data flow, ensuring that users have up-to-date information.
4. Design with User Experience in Mind
User experience (UX) should be a priority. A cluttered, difficult-to-navigate portal will frustrate users and reduce engagement. Invest time in a clean, intuitive design that makes it easy for users to find what they need.
5. Test and Iterate
Before launching your website portal, conduct thorough testing to ensure all functionalities work as expected. Gather feedback from beta users and make necessary improvements. Once the portal is live, continue to monitor its performance and gather user feedback for future updates.
Conclusion
A website portal is more than just a gateway to information; it’s a powerful tool for communication, collaboration, and data management. From businesses to educational institutions, and governments to communities, the use of portals can greatly improve user experience, productivity, and overall operational efficiency.
As digital transformation continues to reshape the way we interact with information, having a website portal that meets the needs of your users is critical. By understanding its core features, benefits, and applications, organizations can leverage the power of website portals to stay competitive and efficient in an increasingly digital world.
With the right approach, a website portal becomes an invaluable asset, offering secure, streamlined access to the information and tools users need to succeed.


